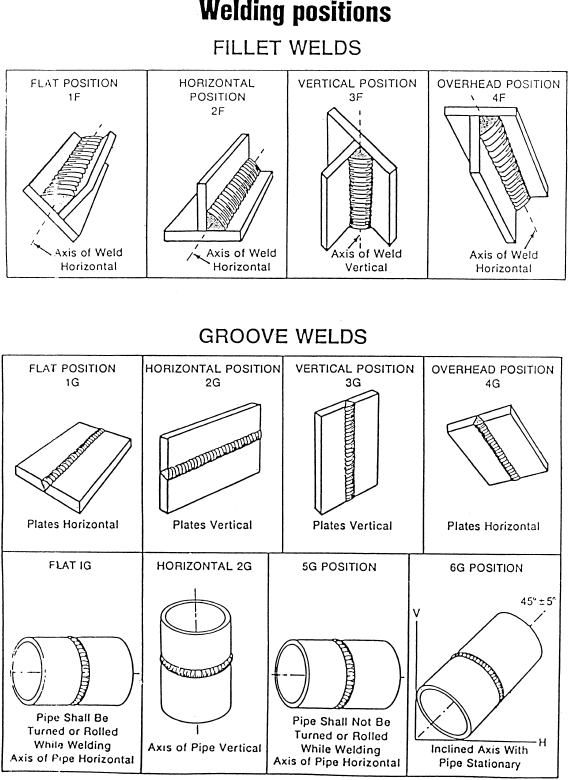
Welding Positions
|
It is important to know the different positions due to it being used to it being used to qualify welders. For instance if a welder gets qualified with a 6G Position that welder would be qualified to weld in any of the other positions. But if the welder got qualified to weld in the 1G position that welder would only be qualified to weld in the 1G position. To make sure though that you are qualifying your welders properly make sure to read the code you are testing to. Also getting qualified in a certain position does not mean that you are qualified to weld on all materials and all thickness'. The thickness' and materials should be determined by the code you are qualifying to.
Below are links to the different types of welding positions. |